New research from the University of the Sunshine Coast has found a decline in the number, size and diversity of Queensland’s apex sharks, marking a “significant shift” in our coastal ecosystems.
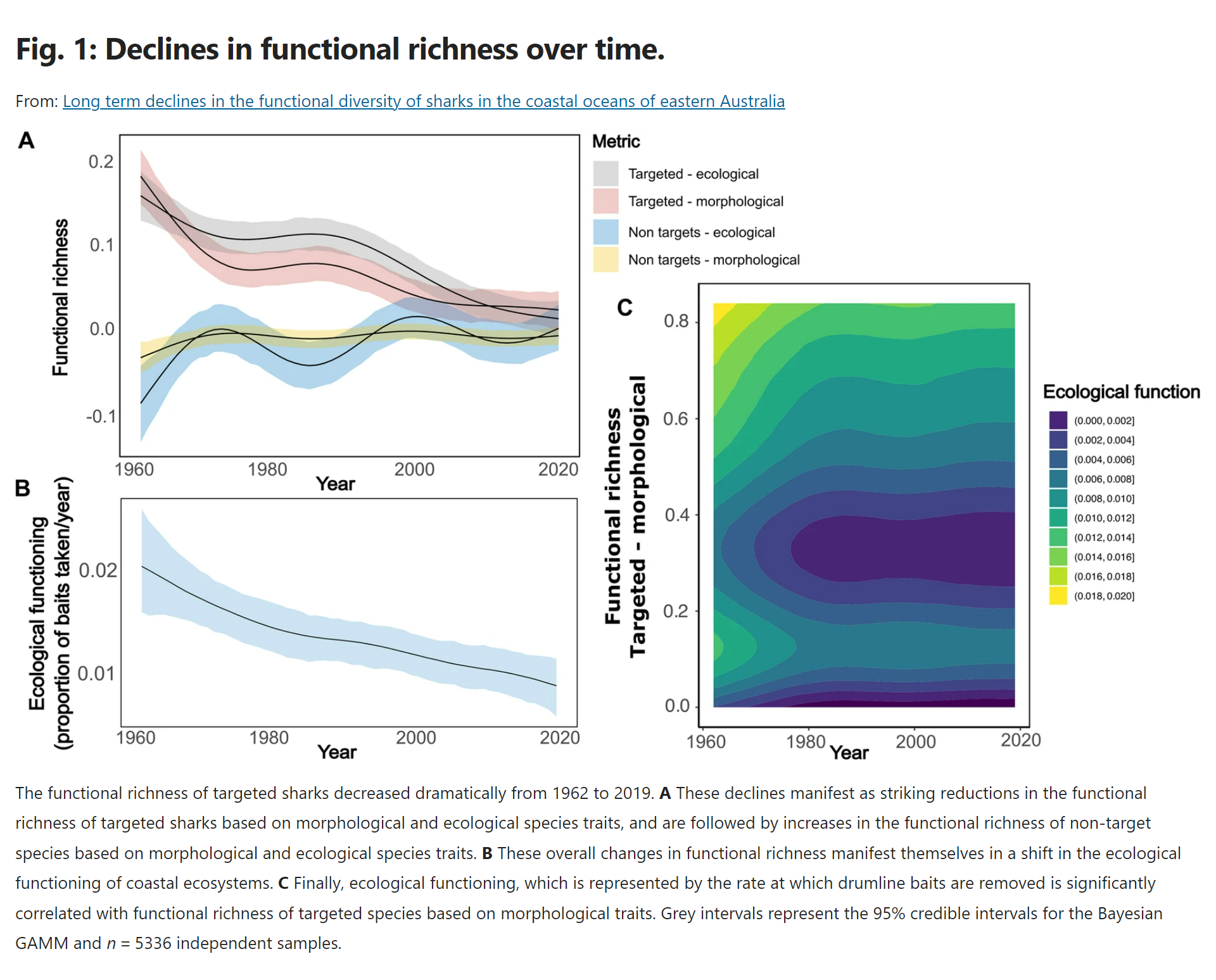
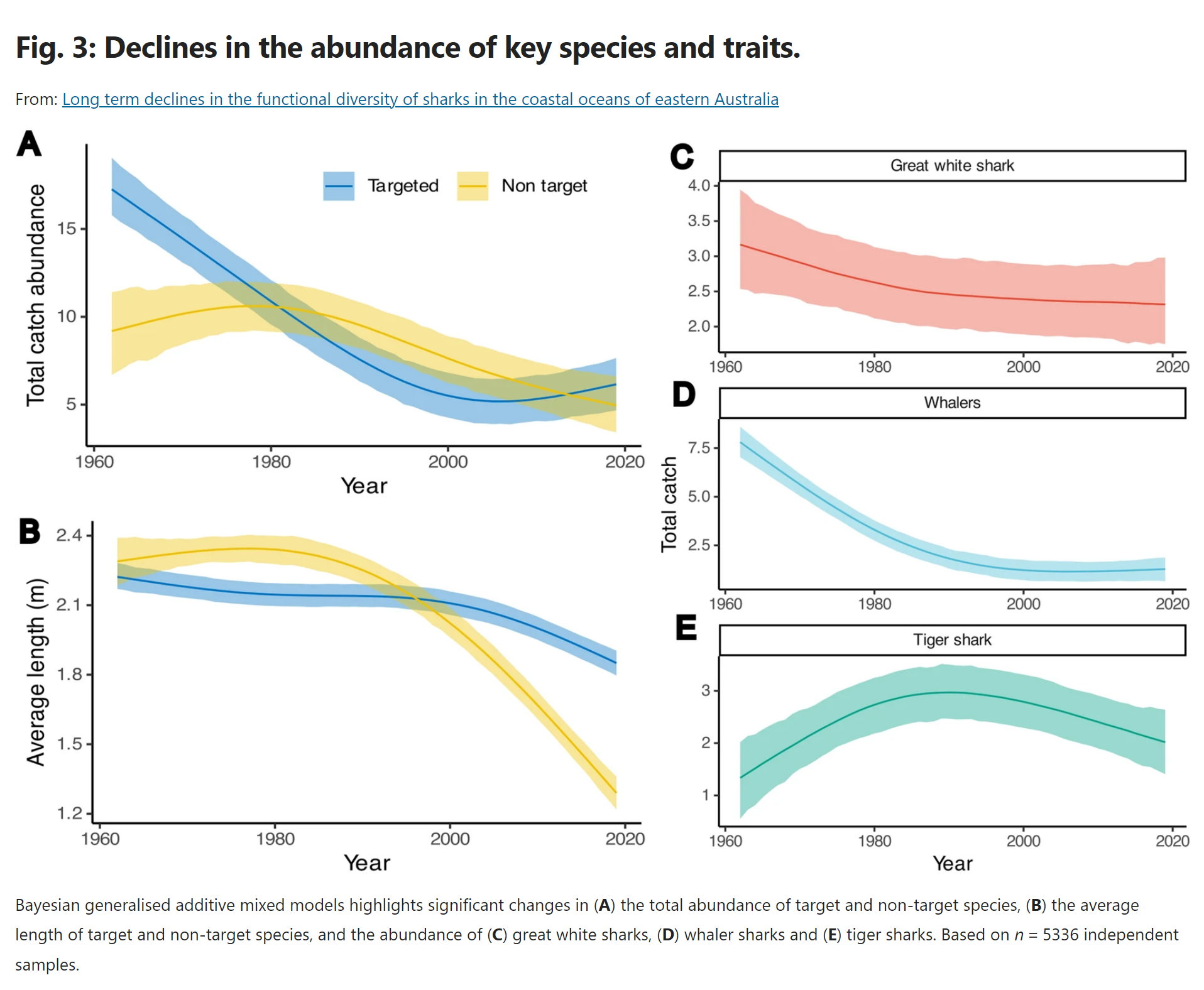
Lead author Dr Chris Henderson and a team of researchers analysed more than 60 years of catch data from Queensland’s Shark Control Program (QSCP), noting a substantial loss in the functional diversity of targeted species like tiger sharks, great whites and whalers.
“There’s been a range of studies looking at declining shark numbers, but we wanted to look at it from an ecosystem perspective, and that is what looking at changes in functional diversity allows us to do,” Dr Henderson said.
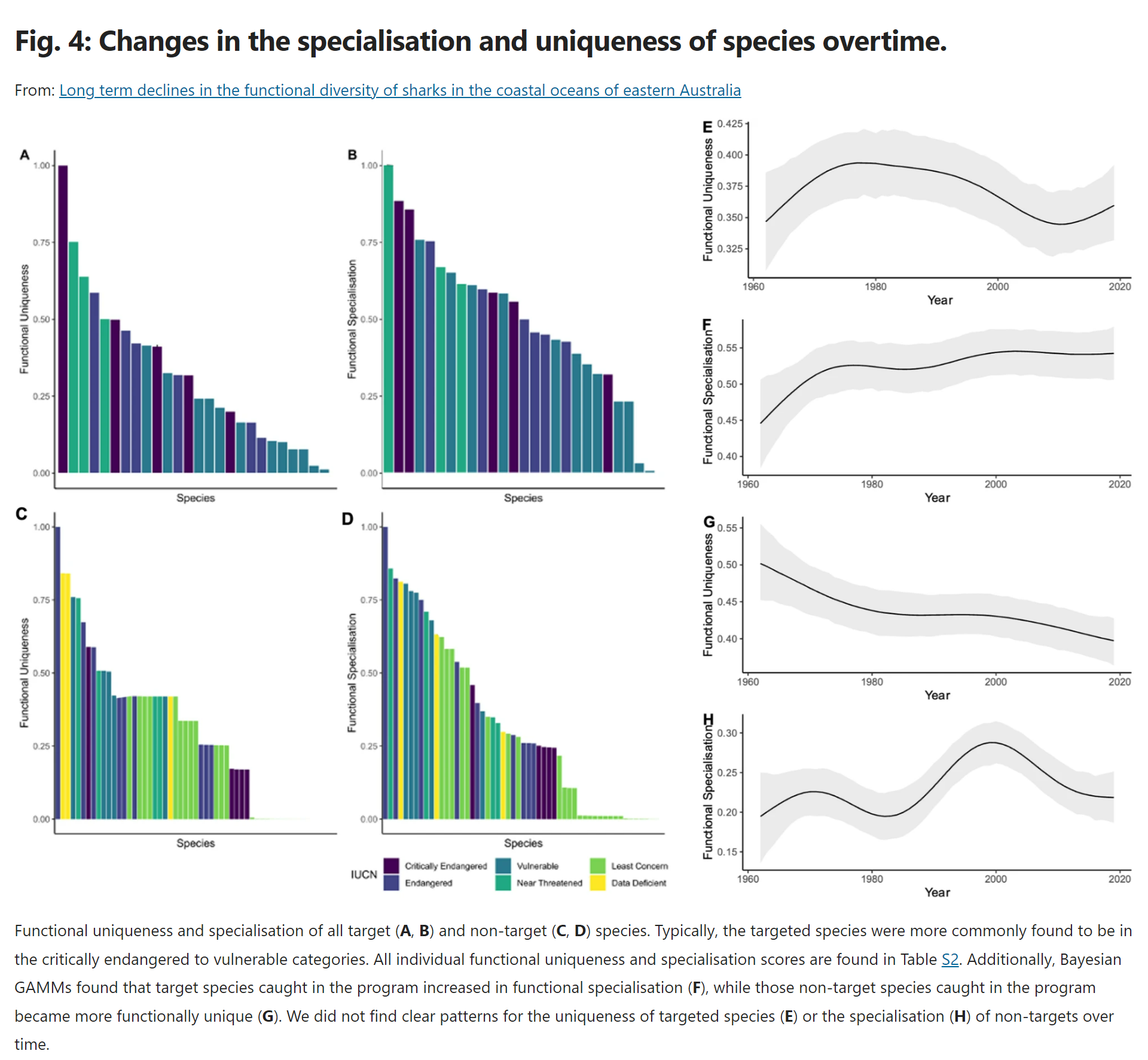
“And what we’ve seen is a decline over time in the abundance and more crucially, the diversity of targeted apex shark species, which means we are at risk of losing sharks that perform crucial roles in our coastal ecosystem, reducing its functioning and resilience.”

Bachelor of Animal Ecology
Study animals in their natural habitats and learn how we can protect wildlife in a changing environment.
It’s not just the apex sharks that are experiencing turbulence.
The size and number of non-targeted sharks caught by the QSCP, like reef sharks, has also declined.
But despite this there’s actually been an increase in the functional diversity of these non-targeted species being caught.
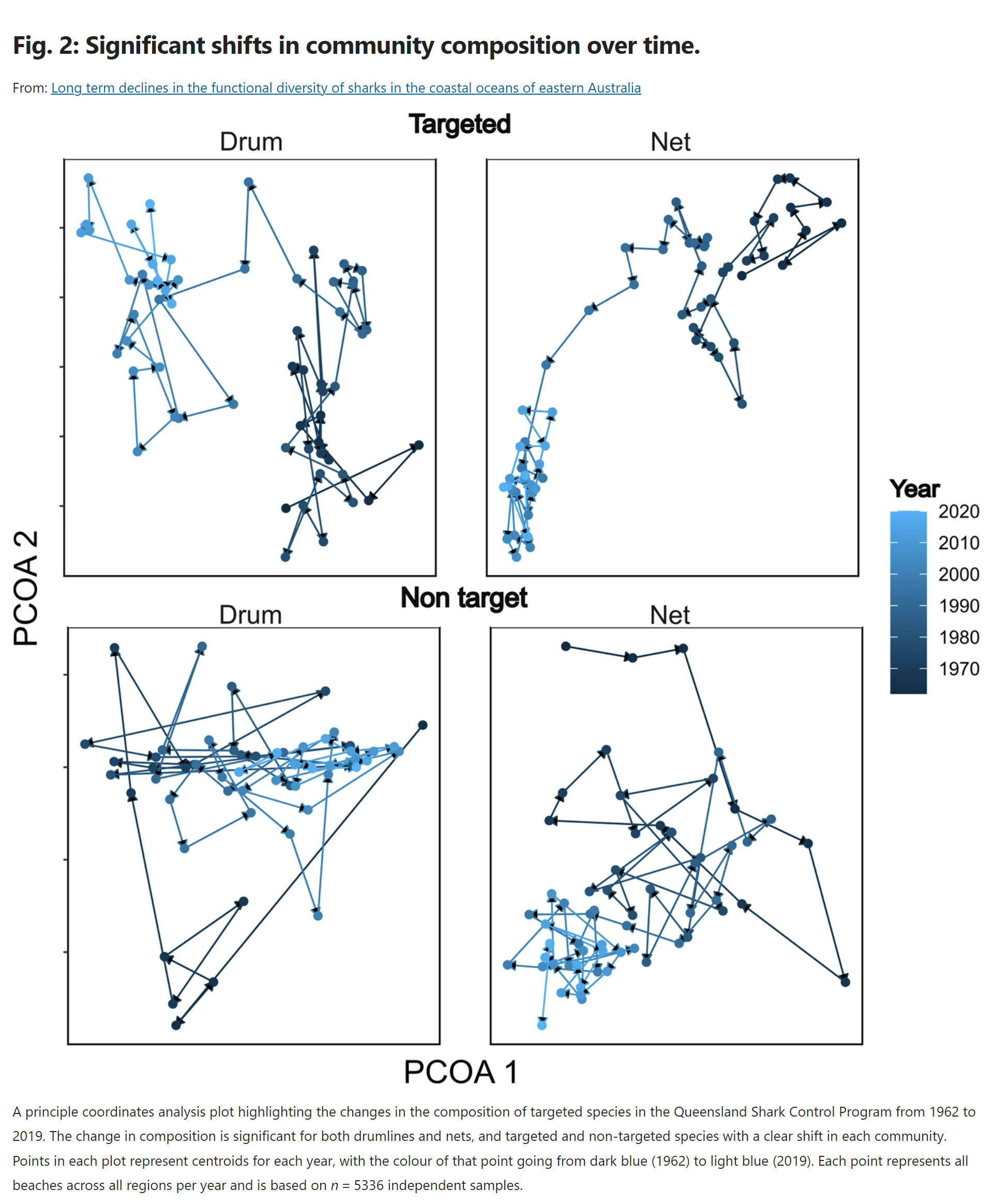
Dr Henderson said this indicates a fundamental change in the composition of species in our coastal ecosystems.
“This tells us that we are having a significant impact on our coastal ecosystems – across the whole food web,” Dr Henderson said.
“Maintaining the different roles that species fulfil in the coastal food web is crucial for balancing the populations of a whole number of different species. Great whites, tiger sharks and reef sharks all affect the populations of different prey species, which in turn suppress the abundance of species below them. It has a ripple effect.
“This significant shift in our shark populations likely reflects the combined impacts of both large-scale regional and international harvesting pressures on fish populations.”
While a useful tool for monitoring shark populations, the Queensland Shark Control Program has also invariably played a part in their decline.
Dr Henderson said the program should continue transitioning away from mesh nets towards more targeted methods in a bid to keep Queenslanders safe.
“This aim of the program is to remove large sharks from the coast to improve swimmer safety, but this has significant impacts on the health of our oceans,” Dr Henderson said.
“The QSCP managers are aware of the broader impacts of the program, and this is highlighted by the change in focus from nets to drumlines over the time of the program. Continuing this transition will be crucial for maintaining many important functional roles in the coastal ecosystem.”

Bachelor of Environmental Management
Become an environmental manager with this course where you’ll learn how to minimise human impacts on the environment, manage resources sustainably, and conserve and restore habitats, biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Media enquiries: Please contact the Media Team media@usc.edu.au